Within the distant Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, a uncommon fungus grows inside useless caterpillars. In conventional Chinese language drugs, this parasitic fungus is prized for its purported medicinal results. Often known as Ophiocordyceps sinensis – colloquially, caterpillar fungus or “Himalayan gold” – it may well fetch astronomical costs on the natural drugs market: as much as US$63,000 per pound.
Ophiocordyceps sinensis fungus is a parasite that targets the caterpillar that’s the larva of the ghost moth. The method begins in late summer season to early fall, when fungal spores infect the caterpillars. Over time, fungal filaments referred to as mycelia slowly unfold out and devour the caterpillars from inside, turning them into hardened, mummified shells by winter. When spring arrives, the fungus enters its remaining stage: A grasslike fruiting physique sprouts from the preserved caterpillar’s head and pushes up by the soil.
A lady shows the fungus on the market at a market. The fungus sprouts from the caterpillar’s head.
Kevin Frayer/Getty Photos Information through Getty Photos
Whereas many conventional Chinese language/natural drugs shoppers are drawn to the fungus for its supposed well being advantages, my curiosity lies in a darker facet of its harvest: the lethal relationship between caterpillar fungus assortment and lightning strikes. As a meteorologist, I examine lightning and its impacts world wide. A couple of components come collectively to make the state of affairs on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau so harmful.
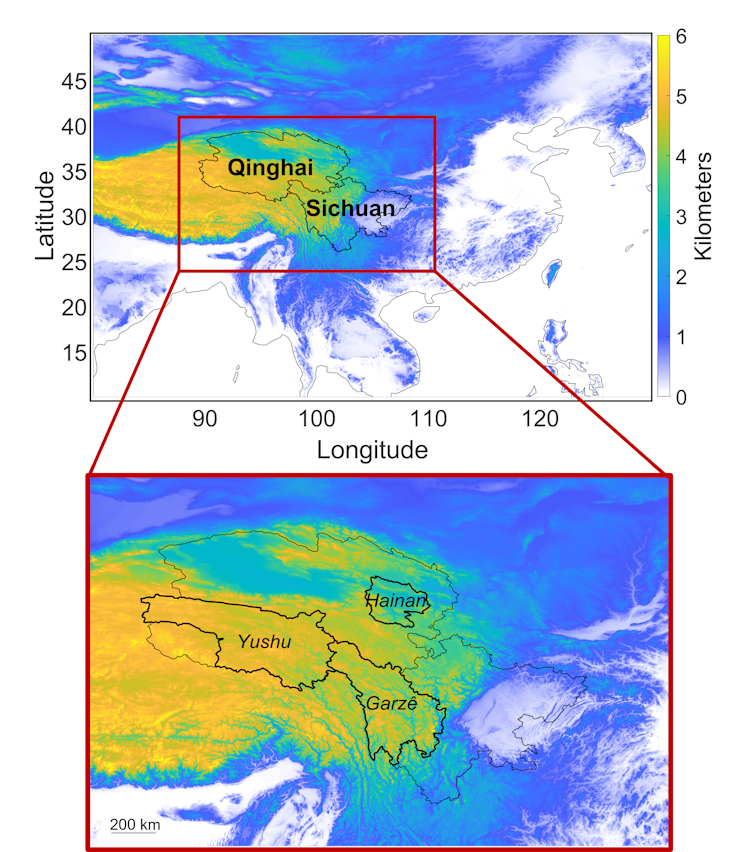
Boundary and topography (elevation depicted by shade) of Qinghai and Sichuan provinces (prime), together with the Yushu, Hainan and Garzˆe Tibetan autonomous prefectures (backside) of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, the place most lightning-strike deaths and accidents occurred.
© 2024 American Meteorological Society (AMS). From Zhang and Holle in Climate, Local weather, and Society.
A lethal harvest
Folks hunt for this fungus throughout late spring and summer season, precisely when lightning strikes are commonest in these mountains. Villagers usually spend weeks scouring the rugged mountains for this treasured useful resource, generally as much as 16,400 toes (5 kilometers) above sea stage. That’s an altitude of greater than 3 miles.
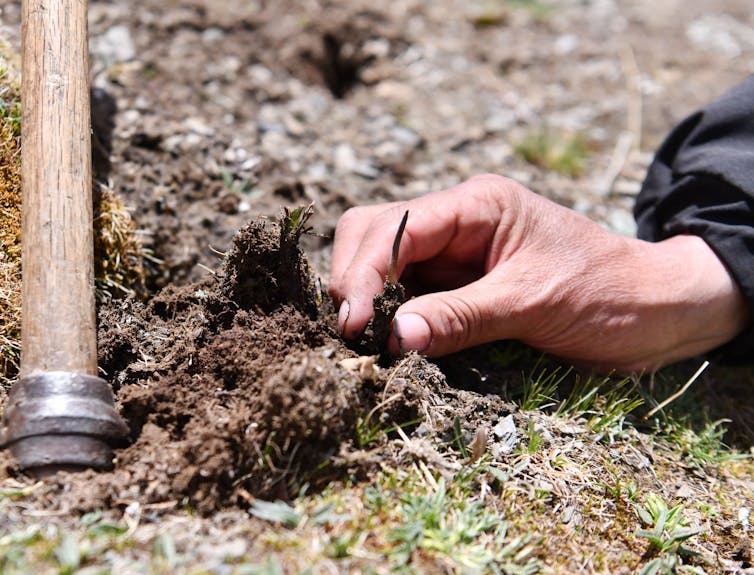

A collector plucks a caterpillar from the bottom. The parasitic fungus has sprouted from the caterpillar’s head.
Jigme Dorje/Xinhua Information Company through Getty Photos
At these heights, the climate can change immediately, and there’s nowhere protected to cover from storms. Whereas this space doesn’t get as many lightning strikes as some components of Asia, it’s nonetheless harmful sufficient to be a critical menace throughout these essential harvesting months.
Tragically, caterpillar fungus searching has led to no less than 31 lightning-related deaths and one other 58 lightning-related accidents previously decade, in keeping with the yearbooks of Chinese language meteorological hazards (中国气象灾害年鉴) and authorities web sites, together with the China Meteorological Administration and the Nationwide Catastrophe Discount Heart of China.
In Might 2022, seven villagers from China, together with a younger youngster, had been killed by lightning whereas harvesting the fungus. The next 12 months, three folks from Nepal had been injured by lightning when gathering the fungus and needed to be rescued by helicopter after spending days stranded within the mountains.
In our latest examine, my colleague Ronald Holle and I discovered that the population-weighted lightning fatality charges within the fungus-collection hotspots of Yushu and Garze counties, positioned within the Sichuan Province of China, are staggering – 10 to twenty occasions greater than the already elevated charges in China general. These numbers are on par with a number of the most lightning-prone areas of Africa, the place there’s little lightning-safe infrastructure or security schooling.
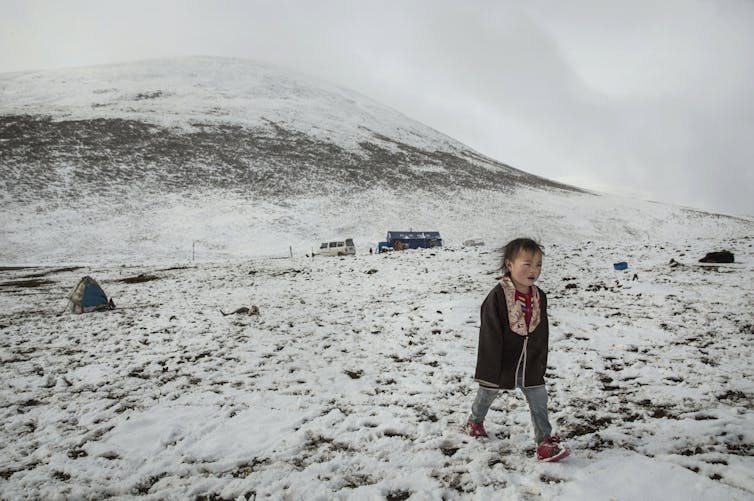

A younger boy walks exterior a brief camp arrange by caterpillar fungus harvesters.
Kevin Frayer/Getty Photos Information through Getty Photos
However lightning isn’t the one menace these villagers face within the mountains. They may encounter hail, heavy rains, robust winds and different extreme climate. The advanced terrain makes climate patterns extremely dramatic and unpredictable. Making issues even worse, cellphone indicators and different communication choices are restricted or nonexistent, leaving villagers minimize off from climate hazard alerts.
They may additionally face threats from wild animals and dangerous mountain slopes. In a single tragic case, a collector was struck by lightning and fell to his demise on steep terrain. Medical care is never out there. When accidents happen, it could be days earlier than assist arrives.
Why take the danger?
All of it comes right down to the high-risk, high-reward nature of caterpillar fungus assortment.
For native villagers, the potential rewards of harvesting caterpillar fungus are important. With restricted earnings alternatives on this distant area, many see the fungus commerce as their greatest hope for survival. They face a tricky alternative: danger their lives or sink into poverty.
Enhancing lightning security schooling and infrastructure are essential however removed from simple. Any actual change would take quite a lot of funding.
Whereas the native authorities does manage some lightning security schooling, these mountain communities are remoted and the data is usually outdated. And there’s merely no sensible approach to set up enough lightning safety throughout the huge, rugged terrain the place the fungus is collected.
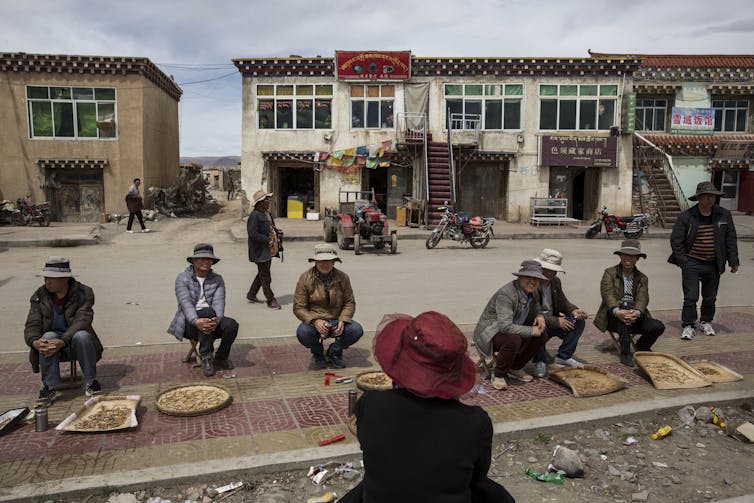

Earnings from the brief assortment season will be crucial for folks within the area.
Kevin Frayer/Getty Photos Information through Getty Photos
A fragile pursuit
The atmosphere is struggling, too. With so many individuals looking for the fungus, they’re damaging the fragile mountain soil, reducing down timber for firewood and leaving trash at their camps.
Years of overharvesting have pressured collectors to spend extra time within the mountains to seek out sufficient fungus, rising their publicity to lightning and the fungus’s decline. Scientists warn that if this aggressive harvesting continues, the fungus would possibly disappear utterly within the subsequent few a long time.
There could be some hope. Researchers are exploring methods to domesticate the fungus as a doable substitute for the wildly harvested selection. In the meantime, governments in China, India, Nepal and Bhutan have applied rules to guard the sustainability of caterpillar fungus.
However any resolution might want to handle the underlying financial and academic inequities on this distant area, opening up new alternatives for these communities to make a residing so that they don’t have to danger their lives chasing “Himalayan gold.”